Scheduling Problems Examples
P.E.R.T. Example
Given the following tasks and their dependencies:
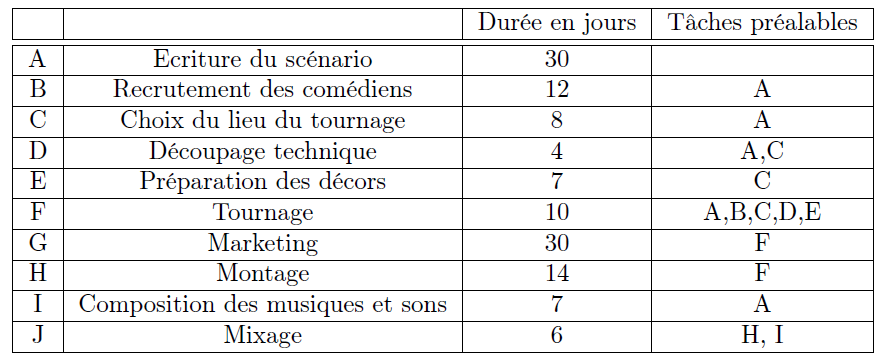
Detailed Explanations
Explanations (dependencies)
- Starting from Start
- The first state $1$ is achieved after completing $A(30)$
- $B$, $C$, and $I$ are only dependent on $A$, meaning they require the state $1$.
- $D$ is dependent on $A$ and $C$, meaning it requires the state $3$.
- Since we are entering state $10$ with $I$ and state $9$ is dependent (for $J$) from $I$, we are using a directed dotted arrow
- ...
Note: we removed (A, F), (A, D), (C, F) because of redundancy.
Explanations (early/last start)
- $Start$ early start value is always 0
- $1$ early state is $0 + 30$ (previous + A cost)
- $6$ early state is $38 + 4$ (previous 38 + D cost)
- ...
As for the last start, starting from the End:
- $End$ last_start value is its early_start value
- $9$ last_start is $85-6=79$ (End's last_start minus J cost)
- $3$ last_start is $min(45-7, 45-4)=38$ (4's last_start minus E cost, and resp. 5's and D)
- ...
Explanations (free/total margin)
- $9$ total margin is simply $79-69=10$
- $10$ total margin is simply $79-37=42$
- ...
As for the free margin:
- $9$ free margin is $x + 69 + 6 \le 85 \Leftrightarrow x=10$
- $10$ free margin is $x + 37 + 0 \le 69 \Leftrightarrow x=32$
- $5$ free margin is $x + 42 + 0 \le 45 \Leftrightarrow x=3$
- ...
Explanations (note)
The critical path is $(Start, A, C, E, F, G, End)$.
The resulting P.E.R.T diagram is:
Metra potential Example
Given the following tasks and their dependencies:
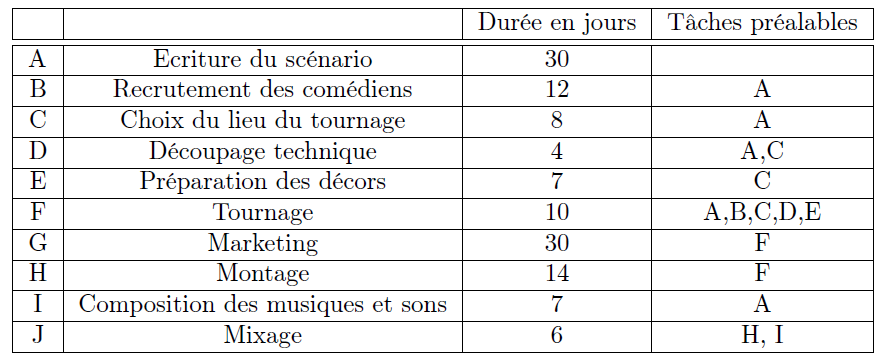
Detailed Explanations
Explanations (dependencies)
- We create one vertex per task
- And we add every edge.
- As $C$ needs $A$, then we have $A \to C$. Since the duration of $A$ is $30$, then the weight is $30$.
- $D$ needs $C$ and $A$, but $C$ needs $A$, so $D$ only needs $C$ (redundancy)
- ...
Explanations (early/last start)
- $C$ early start is $A$ early start + $A$ cost: $0+30=30$
- $D$ early start is $C$ early start + $C$ cost: $30+8=38$
- ...
As for the last start, starting from the End
- $End$ last_start is early_start value
- $J$ last_start is $85-6=79$ (End last_start minus $J$ cost)
- $C$ last_start is $min(41-8, 38-8)=30$ (D and resp. E last_start minus C cost)
- ...
Explanations (free/total margin)
- The total margin is $\text{last_start-early_start}$
- $J$ total margin is simply $79-69=10$
- $I$ total margin is simply $72-30=42$
- ...
As for the free margin:
- $J$ free margin is $x + 69 + 6 \le 85 \Leftrightarrow x=10$
- $H$ free margin is $x + 55 + 14 \le 69 \Leftrightarrow x=0$
- $I$ free margin is $x + 30 + 7 \le 69 \Leftrightarrow x=32$
- $D$ free margin is $x + 38 + 4 \le 45 \Leftrightarrow x=3$
- ...
Explanations (note)
The critical path is $(Start, A, C, E, F, G, End)$.
And the resulting Metra potential diagram is

