Routers
A router is a device usually connecting a LAN network with a WAN network, while more generically, it connects two networks.
A router is a type of Gateway with the main purpose of delivering data, unlike a gateway which focuses on connecting networks.
It routes packets, meaning, it selects the best path to send traffic. This choice is determined by algorithms such as:
- 💨 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- ☠️ Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- 🌿 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- ...
These algorithms are using information such as the shortest number of devices to reach the target (hops), the reliability of the path (are packet often lost?), the network speed (fibre?)...
Routing table
A router will use a routing table to determine
- if we can send the packet directly to the destination
- or, which machine can we delegate the delivery
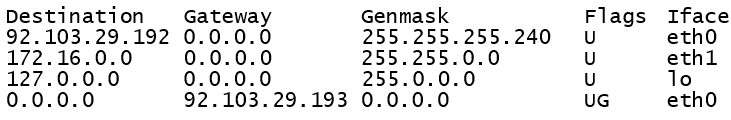
Destination is a range of IPs. It must be used with GenMask (NetMask) to identify what's the range. A destination of 0.0.0.0 with the GenMark 0.0.0.0 means every IP. It's used as a default rule.
⚠️️ The order of rules is important, the first matching one is used.
Gateway: if the IP is within a destination, the message is sent to the gateway. If the gateway is 0.0.0.0, then it means that the device is directly connect to the machine.
Gateways associated with the default rule are usually IP addresses ending with .1 or .254, while it's not mandatory.
The notion of "gateway" used in routing table, is not necessarily a Gateway device. It could be a Router...
IFace is the interface used to send the packet.

